YesVitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a critical role in keeping your body and mind functioning at their best. Unlike most nutrients, vitamin D functions as both a vitamin and a hormone, impacting everything from bone development and immune defense to mood regulation and muscle strength. Yet, despite its importance, vitamin D deficiency remains a global health issue, affecting millions—even in sunny regions.
Table of Contents
How Does Vitamin D Work in the Body?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble nutrient that helps regulate the absorption of calcium and phosphate—two minerals vital for healthy bones, teeth, and muscles. There are two primary forms:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) – found in plant sources
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) – synthesized in your skin through sunlight and found in animal sources
Once inside the body, vitamin D is converted into its active form (calcitriol), which then helps carry out multiple biological processes.
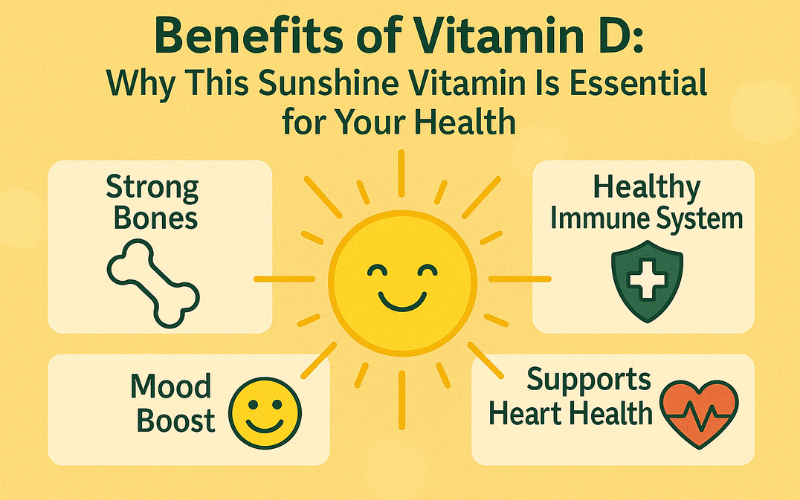
Key Benefits of Vitamin D for Your Body and Mind

Discover how Vitamin D supports strong bones, a healthy immune system, and boosts your mood naturally.
1. Stronger Bones and Teeth
Vitamin D enhances calcium absorption, which is essential for building and maintaining bone density. It helps prevent fractures, bone pain, and deformities.
2. Muscle Strength and Function
It supports muscle contraction and recovery, reducing the risk of falls and improving physical performance, especially in older adults.
3. Immune System Support
Vitamin D helps activate immune defenses and may reduce the risk of infections like colds, flu, and even certain autoimmune conditions.
4. Mental Health and Mood Regulation
Low vitamin D levels are associated with symptoms of depression, anxiety, and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). Adequate levels may enhance mood stability.
5. Reduced Inflammation
It has anti-inflammatory effects, which may benefit those with chronic inflammatory diseases like arthritis or asthma.
6. Disease Prevention
Studies suggest vitamin D may play a role in lowering the risk of conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and multiple sclerosis.
Vitamin D and Bone Health: Preventing Rickets and Osteomalacia
One of vitamin D’s most vital roles is bone mineralization. Without it, bones become soft and brittle. Deficiency can lead to:
- Rickets: A childhood disorder that causes bone deformities
- Osteomalacia: A softening of bones in adults that leads to pain and weakness
Yes Vitamin D ensures that dietary calcium is properly absorbed and deposited into bones.
Vitamin D for Immune Support and Infection Resistance
Vitamin D helps modulate immune responses, making it a frontline nutrient in protecting against bacterial and viral infections. Research shows that people with adequate vitamin D levels may be less likely to catch common colds, flu, and even respiratory illnesses. This is especially crucial during winter months when sunlight exposure is limited.
Mental Health Benefits: Can Vitamin D Boost Your Mood?
Emerging evidence links low vitamin D levels to poor mental health outcomes, including depression, fatigue, and brain fog. This is partly due to vitamin D’s role in serotonin production and brain function.
- People with Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) often benefit from vitamin D supplementation.
- Low levels may also worsen symptoms of anxiety and cognitive decline in older adults.
Who Is at Risk of Vitamin D Deficiency?
Several groups are more likely to have inadequate vitamin D levels:
- Infants and children, especially those exclusively breastfed without supplements
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Older adults, due to less efficient skin synthesis
- People with darker skin, who produce less vitamin D from sunlight
- Indoor workers, shift workers, or those living in northern climates
- People with kidney or liver disease, or those on medications that impair absorption
How to Get Enough Vitamin D: Sunlight, Food, and Supplements
- Aim for 10–30 minutes of midday sunlight several times a week (depending on skin tone and location)
- Avoid sunscreen during this period, but don’t overexpose
Dietary Sources
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Egg yolks
- Fortified dairy, plant milk, and cereals
- Cod liver oil
- Mushrooms exposed to sunlight
Supplements
- Vitamin D3 is more effective than D2 at raising blood levels
- Especially important in winter or if you have limited sun exposure
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need Daily?

The recommended intake varies based on age and health status:
- Infants (0–12 months): 400 IU (10 mcg)
- Children and adults up to 70: 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults over 70: 800 IU (20 mcg)
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: 600 IU (15 mcg)
The upper safe limit is 4000 IU/day unless advised otherwise by a healthcare professional.
Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Watch for these common symptoms:
- Fatigue and low energy
- Bone or back pain
- Frequent illness or infections
- Muscle weakness or cramps
- Hair loss
- Low mood or depression
A simple blood test can confirm your vitamin D status.
Conclusion:
From stronger bones to better immunity and improved mood, the benefits of vitamin D are wide-ranging and well-documented. To stay healthy, ensure you’re getting enough through a mix of sunlight, diet, and supplements—especially if you’re at risk for deficiency. Small changes today can lead to big improvements in your long-term well-being.