Creatine monohydrate is one of the most popular and researched supplements in the fitness world. But how does creatine monohydrate work in the body to enhance performance, muscle growth, and recovery? In this detailed guide, we’ll explain the science behind creatine, its mechanism of action, and why it is essential for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Table of Contents
What is Creatine Monohydrate?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in muscle cells, produced by the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. It can also be obtained through dietary sources like red meat and fish. Creatine monohydrate is the most common and effective supplemental form, widely used for its proven benefits in strength, power, and muscle endurance.
How Does Creatine Monohydrate Work in the Body?
Creatine monohydrate works by increasing phosphocreatine stores in your muscles, helping regenerate ATP the body’s primary energy source. This boosts strength, power, and endurance during high-intensity exercise. It also enhances muscle hydration, supports recovery, and may improve cognitive performance by supplying quick energy to brain cells.
Role in ATP Energy Production
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is the primary energy currency of the body. During high-intensity activities like lifting weights or sprinting, ATP depletes rapidly. Creatine helps replenish ATP by donating a phosphate group through phosphocreatine (PCr), enabling sustained energy bursts.
Muscle Phosphocreatine Stores & Energy Boost
When you supplement with creatine monohydrate, your muscle phosphocreatine stores increase, allowing for quicker regeneration of ATP. This results in enhanced power output, improved workout performance, and reduced fatigue.
Impact on Muscle Cell Hydration (Cell Volumization Effect)
Creatine draws water into muscle cells, increasing cellular hydration. This not only enhances muscle fullness and size but also creates an environment conducive to muscle protein synthesis.
Effects on Strength & Exercise Performance
By providing immediate energy reserves, creatine monohydrate improves strength, explosiveness, and exercise performance, especially in short-duration, high-intensity activities.
Brain Creatine Stores & Cognitive Benefits
Emerging research shows that creatine supplementation also elevates brain phosphocreatine levels, potentially supporting memory, focus, and cognitive function, particularly in vegetarians and older adults.
Scientific Breakdown: Creatine’s Journey in the Body
Creatine’s journey in the body begins with rapid absorption, conversion into phosphocreatine, and delivery to muscle cells to regenerate ATP for instant energy.
Absorption Process
After ingestion, creatine is absorbed in the small intestine and enters the bloodstream. From there, it is transported to muscle tissues through specific creatine transporters.
Conversion to Phosphocreatine (PCr)
Once inside the muscle cells, creatine is converted into phosphocreatine, which serves as a rapid phosphate donor to regenerate ATP during intense physical exertion.
ATP Replenishment During High-Intensity Workouts
This entire process enhances the muscle’s ability to perform repeated bouts of explosive activity, making creatine an essential energy buffer.
Creatine Monohydrate Benefits for Athletes & Fitness Enthusiasts
- Increased muscle mass and strength
- Enhanced exercise performance and endurance
- Faster post-exercise recovery
- Reduced muscle cramping and injuries
- Cognitive performance improvements
Daily Dosage: How Much Creatine Does Your Body Need?
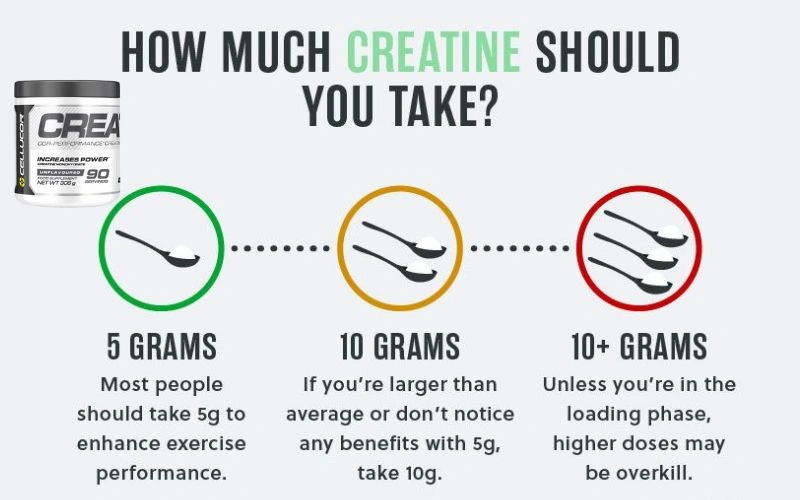
Your body typically needs 3–5 grams of creatine monohydrate daily to maintain optimal muscle stores. This amount supports consistent ATP regeneration, improved strength, and better workout performance. Athletes may use a short loading phase of 20 grams per day for faster saturation, but it’s not necessary for long-term benefits.
Loading Phase vs Maintenance Phase Explained
A typical loading phase involves taking 20g per day, divided into 4 doses, for 5-7 days to quickly saturate muscle stores. Post-loading, a maintenance dose of 3-5g daily is recommended.
Can You Take Creatine Every Day?
Yes, creatine monohydrate should be taken daily for sustained benefits. Consistency is key for maintaining elevated phosphocreatine levels.
Hydration Importance with Creatine Supplementation
Adequate water intake is essential as creatine increases intracellular water retention, which supports optimal performance and reduces risks of dehydration.
What Happens When You Stop Taking Creatine?
When you discontinue creatine supplementation, muscle creatine stores gradually return to baseline within 3-4 weeks. You might notice a slight reduction in muscle fullness (due to water loss) and marginal declines in explosive strength.
Common Myths about Creatine Monohydrate
Many common myths about creatine monohydrate like causing kidney damage, dehydration, or excessive weight gain—are not supported by scientific evidence.
Creatine Causes Water Retention and Fat Gain
Fact: Creatine draws water into muscle cells, not under the skin.
-
This intracellular hydration supports performance and muscle growth.
-
It does not cause fat gain or bloating.
Creatine Damages Kidneys and Liver
Fact: Research consistently shows creatine is safe for healthy individuals.
-
No adverse effects on kidney or liver function when used at recommended doses.
-
Clinical studies, even long-term, report no organ damage.
Creatine Leads to Hair Loss
Fact: There is no solid scientific evidence linking creatine to hair loss.
-
One small study suggested a possible increase in DHT, but results were inconclusive.
-
No research proves creatine directly causes hair shedding.
Is Creatine Safe? Side Effects and Precautions
Creatine monohydrate is safe for most healthy adults. Minor side effects like bloating or stomach cramps can occur, especially during loading phases. Individuals with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions should consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation.
Best Time to Take Creatine for Maximum Absorption

While creatine can be taken at any time, consuming it post-workout with a carbohydrate and protein meal may optimize muscle uptake. However, consistency in daily intake is more important than precise timing.
Choosing the Right Creatine Supplement: Why Monohydrate is King
Creatine monohydrate remains the gold standard due to its extensive research, affordability, and proven effectiveness. Alternatives like creatine ethyl ester or buffered creatine lack sufficient evidence.
Creatine and Brain Health: Emerging Research
Recent studies suggest creatine supplementation may improve cognitive functions like memory, attention, and mental clarity, especially in populations with lower natural creatine levels.
Does Creatine Work Differently for Men and Women?
Both men and women benefit from creatine supplementation. However, women may experience slightly lesser water retention and strength gains but still achieve significant performance and recovery improvements.
Creatine for Vegetarians: Why It’s More Effective
Vegetarians tend to have lower baseline creatine stores due to minimal dietary intake, making supplementation even more effective in enhancing muscle saturation and performance.
How Long Does It Take for Creatine to Show Results?
With a loading phase, noticeable improvements in strength and performance may appear within a week. Without loading, benefits typically become evident after 3-4 weeks of consistent use.
How to Combine Creatine with Other Supplements (Whey, Pre-Workout)
Creatine can be effectively combined with whey protein, pre-workouts, and BCAAs to support muscle growth, energy, and recovery. Ensure to monitor total supplement intake and hydration levels.
FAQs “how does creatine monohydrate work in the body
1. How does creatine monohydrate work in the body?
Creatine monohydrate increases phosphocreatine levels in your muscles, helping regenerate ATP, the primary energy source during high-intensity activities.
2. Does creatine monohydrate help in muscle growth?
Yes, creatine monohydrate supports muscle growth by increasing workout performance, allowing you to lift heavier weights and perform more reps.
3. How long does it take for creatine monohydrate to work?
If you follow a loading phase (20g/day), creatine saturates muscles in 5-7 days. Without loading, noticeable benefits appear within 3-4 weeks of consistent daily intake (3-5g/day).
4. Does creatine monohydrate cause water retention?
Creatine monohydrate draws water into muscle cells, leading to mild water retention that increases muscle fullness.
Conclusion
Creatine monohydrate is a safe, effective, and scientifically backed supplement that enhances energy production, muscle growth, and recovery. Its benefits are well-documented, making it a valuable addition to any fitness routine. Consistent intake, adequate hydration, and proper dosage are key to maximizing its effects.
Ready to experience the benefits of creatine monohydrate? Shop now for authentic creatine supplements at Nutritionalworld.com.pk and take your fitness to the next level!



























