A strong immune system depends on more than just vitamins and minerals. Amino acids, especially glutamine, are essential for immune resilience. Glutamine for immune system health has gained attention because immune cells rely heavily on this amino acid for energy and proper function.
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the body, but during physical stress, infection, surgery, or intense exercise, natural production may not meet increased demand. Understanding how glutamine supports immunity helps individuals make informed nutritional decisions, particularly during periods of higher physiological stress.
Table of Contents
Glutamine Metabolism in Immune Cells
Immune cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils require constant energy to function efficiently. Glutamine acts as a primary metabolic fuel for these cells, supporting their growth, division, and activity. During periods of stress, illness, or intense physical demand, glutamine levels may decline, making targeted supplementation useful. High-quality glutamine supplements, such as ELEV Glutamine Extreme 300g available.
Unlike many other tissues, immune cells use glutamine at very high rates, even more than glucose in some cases. When glutamine availability drops, immune cell performance can decline, leading to reduced immune responsiveness. This explains why glutamine for immune system support becomes critical during illness or stress.
Role of Glutamine in Immune Cell Function
Glutamine supports several essential immune processes. It aids immune cell proliferation, ensuring the body can rapidly produce white blood cells when needed. It also contributes to cytokine production, which allows immune cells to communicate effectively during infections.
Additionally, glutamine enhances phagocytosis, the process by which immune cells engulf and destroy pathogens. Without sufficient glutamine, these defense mechanisms may weaken, compromising overall immune efficiency.
Glutamine as a Fuel During Physiological and Metabolic Stress
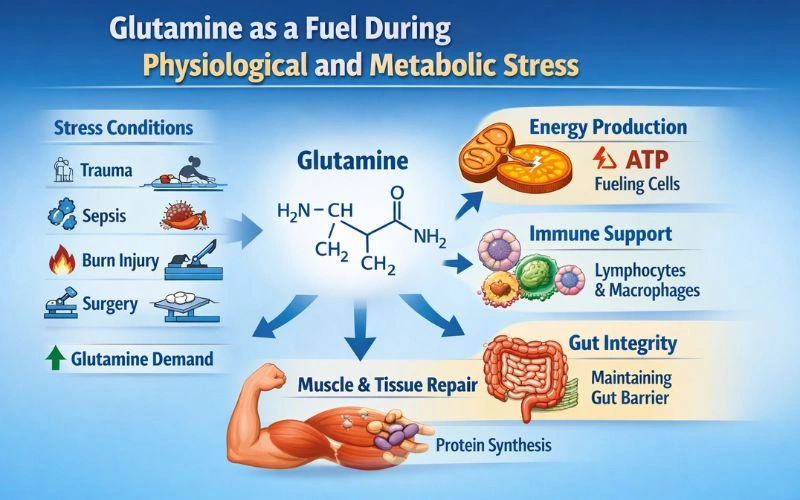
During infection, injury, surgery, or intense physical training, the body enters a catabolic state. In such conditions, glutamine stores are rapidly depleted to meet increased metabolic demands.
Low glutamine levels during stress are associated with immune suppression and slower recovery. Supplementing glutamine during these periods may help restore immune balance, improve recovery, and reduce the risk of secondary infections. This is why glutamine for immune system support is commonly discussed in both clinical nutrition and sports science.
Mechanisms Linking Glutamine and Immune Response
One of the most important mechanisms connecting glutamine to immunity is the gut–immune axis. Glutamine helps maintain the integrity of the intestinal lining, preventing harmful pathogens from entering the bloodstream. During periods of digestive stress or increased immune demand, using a reliable glutamine supplement such as Glutamine 250gm.
It also plays a role in nitrogen transport and cellular signaling pathways that regulate immune responses. By supporting gut barrier function and immune cell metabolism simultaneously, glutamine contributes to a more resilient immune system overall.
Clinical and Physiological Implications of Glutamine
Research suggests glutamine may support immune resilience in individuals under chronic stress, athletes with heavy training loads, and patients recovering from illness or surgery. While glutamine is not a cure or treatment, it supports normal immune function when demands are elevated.
For generally healthy individuals, adequate dietary protein often meets baseline glutamine needs. However, during periods of increased stress, additional glutamine intake may help maintain immune stability and recovery capacity.
Natural Food Sources of Glutamine

Glutamine is naturally present in many protein-rich foods, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, spinach, and cabbage. These foods support everyday glutamine requirements.
However, during illness or high stress, dietary intake alone may not provide sufficient amounts to meet increased immune demands, which is why supplementation is sometimes considered.
Glutamine Supplementation for Immune System Support
Glutamine supplements are commonly used to support immune and gut health during stress. Typical supplemental amounts range from 5–10 grams per day for general support, with higher intakes used short term under professional guidance.
Supplementation should not replace a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle. Individuals with medical conditions should consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation.
Safety, Side Effects, and Precautions
Glutamine is generally considered safe for healthy adults when consumed within recommended ranges. It is well tolerated and does not interfere with normal amino acid metabolism. Some individuals also include complementary amino acid formulas, such as ELEV Argi-Pro.
People with kidney disease, liver disorders, or those undergoing medical treatment should seek professional advice before using glutamine supplements to ensure safety and suitability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does glutamine really support the immune system?
Yes. Glutamine provides essential fuel for immune cells, supports gut barrier integrity, and helps immune cells function efficiently during stress. Research shows that adequate glutamine availability is linked with stronger immune responsiveness, especially during illness or physical strain.
Can glutamine be taken daily for immune health?
For most healthy individuals, daily glutamine intake from food or supplements is safe when used within recommended limits. Daily use may help maintain immune and gut health, particularly during stressful periods, but it should complement a balanced diet.
Is glutamine better than vitamin C or zinc for immunity?
Glutamine, vitamin C, and zinc serve different roles. Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant, zinc supports immune signaling, while glutamine fuels immune cells and gut health. They work synergistically rather than replacing one another.
How long does it take to see immune benefits from glutamine?
Some people notice improved digestion or recovery within a few days. Immune-related benefits often require consistent intake over one to two weeks, especially during periods of physical or metabolic stress.
Is glutamine safe for long-term use?
Long-term glutamine use is generally safe for healthy individuals when consumed responsibly. However, extended high-dose use should be discussed with a healthcare professional to ensure it aligns with individual health needs.
Conclusions and Future Directions
Glutamine plays a vital role in immune cell metabolism, gut health, and recovery during stress. Scientific evidence supports its importance in maintaining immune resilience, particularly when the body faces increased physiological demands. Glutamine for immune system support is best viewed as part of a holistic nutrition and lifestyle approach rather than a standalone solution.
For those looking to support their immune health with trusted nutrition options, explore quality supplements and expert guidance at https://nutritionalworld.com.pk/ and take an informed step toward better overall wellness.