Table of Contents
Can Low Testosterone Cause Weight Gain?
Testosterone, often referred to as the “male hormone,” plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, from regulating muscle mass and bone density to controlling fat distribution. However, when testosterone levels drop below optimal levels, it can lead to a series of physical changes, one of the most common being weight gain.
For many men, unexplained weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area, can be frustrating. Understanding the connection between low testosterone and weight gain is essential for those experiencing this issue. In this article, we’ll explore how testosterone levels influence body weight and discuss how a hormonal imbalance can disrupt metabolism, leading to unwanted weight gain.
What is Testosterone and Its Role in the Body?
Testosterone is a hormone primarily produced in the testes in men and in smaller amounts in women’s ovaries. It plays a vital role in the development of male reproductive tissues and the maintenance of secondary sexual characteristics such as muscle mass, bone density, and body hair. Beyond these physical traits, testosterone also helps regulate a variety of important functions:
- Muscle Mass & Strength: Testosterone is essential for the growth and maintenance of muscle tissue. It promotes protein synthesis, which directly influences muscle strength and size.
- Fat Distribution: Testosterone helps in regulating fat storage in the body. It encourages the storage of fat in certain areas and helps maintain a healthy fat-to-muscle ratio.
- Metabolism: Testosterone affects metabolism by influencing the rate at which the body burns calories. A drop in testosterone can slow down metabolism, making it easier to gain weight.
When testosterone levels are balanced, it supports a lean body composition, healthy energy levels, and overall vitality. However, when testosterone levels drop, the body’s natural ability to regulate weight and maintain muscle mass diminishes, making it easier to gain fat, particularly around the abdomen.
How Low Testosterone Affects Weight Gain
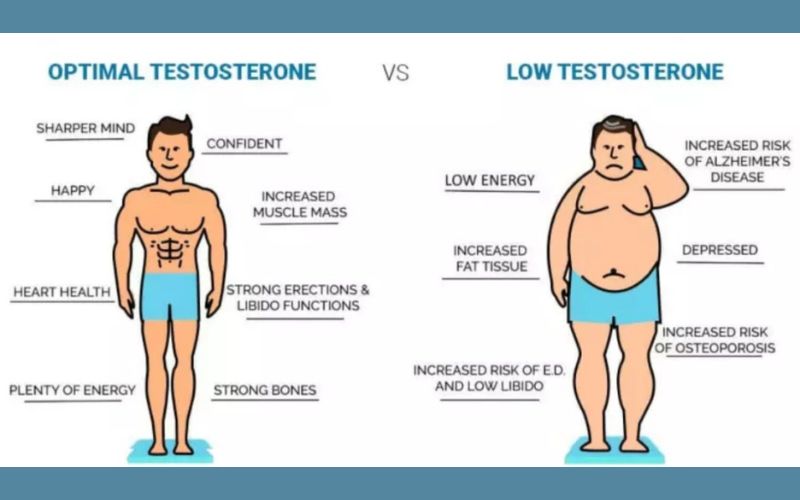
As testosterone levels decline, it can lead to a number of physiological changes that contribute to weight gain. Here’s how low testosterone can affect your body:
- Loss of Muscle Mass: Testosterone is essential for building and maintaining muscle. As levels decrease, muscle mass tends to shrink, resulting in a lower basal metabolic rate (BMR). With a lower BMR, the body burns fewer calories at rest, making weight gain more likely.
- Increased Fat Storage: Testosterone helps regulate fat distribution in the body. Low levels of this hormone can shift fat storage to the abdominal area, which is a common site for weight gain in men with low testosterone.
- Reduced Energy & Physical Activity: Low testosterone can lead to fatigue and a decreased desire for physical activity. This reduced energy expenditure further contributes to weight gain, as the body becomes less active, leading to an imbalance between calorie intake and output.
The combination of muscle loss, increased fat storage, and a slowed metabolism can make it significantly harder to maintain a healthy weight when testosterone levels are low.
The Relationship Between Hormonal Imbalance and Metabolism
Testosterone doesn’t function in isolation; it works in tandem with other hormones that regulate metabolism and energy balance. One key hormone that interacts with testosterone is insulin, which regulates blood sugar and fat storage.
- Testosterone and Insulin Sensitivity: Low testosterone levels have been linked to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can lead to higher insulin levels, which promotes fat storage, especially around the abdominal area.
- Cortisol and Stress: Cortisol, a hormone produced during times of stress, can also affect testosterone levels. Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can reduce testosterone production and lead to weight gain, especially in the belly.
Testosterone works to balance other hormones that play crucial roles in metabolism. When it’s out of balance, these hormonal interactions can lead to metabolic dysfunction, contributing to weight gain.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone Beyond Weight Gain
Low testosterone doesn’t just affect weight – it can influence various aspects of physical and mental well-being. While unexplained weight gain is a common symptom, individuals with low testosterone may experience a range of other effects. Here are some of the key symptoms to look out for:
- Fatigue and Low Energy: One of the hallmark symptoms of low testosterone is extreme fatigue. Without sufficient testosterone, the body lacks the energy to engage in physical activity, leading to a more sedentary lifestyle, which can exacerbate weight gain.
- Mood Swings and Irritability: Testosterone influences mood regulation. A deficiency can lead to feelings of irritability, anxiety, and depression, which can further contribute to weight gain as emotional eating often becomes a coping mechanism.
- Decreased Libido: A noticeable decrease in sexual drive or performance is often reported by men with low testosterone. This decline can be another indicator of hormonal imbalance, which also contributes to the overall decrease in motivation and physical activity.
- Muscle Weakness and Reduced Strength: Testosterone helps in maintaining muscle mass and strength. Low testosterone often leads to a gradual loss of muscle, making it more challenging to maintain a lean physique.
These symptoms, when combined with weight gain, can make it harder to identify the root cause of the problem. Many men struggle with the dual challenges of fatigue and gaining weight, further highlighting the impact of low testosterone on overall health.
How Age and Testosterone Decline Contribute to Weight Gain
Testosterone levels naturally begin to decline as men age, with noticeable drops typically occurring after the age of 30. This gradual decrease in testosterone can lead to several changes in the body, making weight management more challenging as men grow older.
- Metabolic Rate Decline: As testosterone decreases with age, the metabolic rate slows down. This means the body burns fewer calories, making it easier to gain weight, particularly if lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise are not adjusted accordingly.
- Fat Distribution Changes: Older men with low testosterone often notice an increase in abdominal fat. This shift in fat storage can be attributed to reduced muscle mass and the hormonal changes that accompany the decline in testosterone.
- Increased Risk of Insulin Resistance: Aging men with low testosterone are also at a higher risk for developing insulin resistance, which can contribute to both weight gain and the onset of conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Understanding how age-related testosterone decline can affect metabolism and fat storage is important for men looking to manage their weight as they get older.
Scientific Research on Testosterone and Weight Gain

There has been a growing body of scientific research exploring the relationship between testosterone levels and weight gain. Several studies suggest that low testosterone levels contribute directly to an increase in body fat and a decrease in muscle mass.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): Research has shown that testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) can help restore normal testosterone levels in men with low testosterone. In many cases, this therapy not only improves energy levels and mood but also helps in reducing body fat, especially in the abdominal area.
- Body Composition Studies: Studies indicate that men undergoing TRT often experience a significant increase in lean muscle mass and a reduction in body fat percentage. This suggests that correcting low testosterone levels can reverse the negative effects of hormonal imbalances on weight.
- Insulin Sensitivity Improvements: Some studies have also indicated that TRT can improve insulin sensitivity, which may explain why men with low testosterone who undergo treatment often see improvements in both weight and overall metabolic health.
The evidence from scientific research underscores the importance of addressing low testosterone levels to help manage weight and improve overall health.
Treatment Options for Low Testosterone and Weight Gain
For individuals experiencing weight gain due to low testosterone, several treatment options are available. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on individual needs. Here are some common treatments:
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): TRT is one of the most effective ways to restore normal testosterone levels. It is available in several forms, including injections, patches, gels, and pellets.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet and exercise can play a significant role in managing low testosterone levels and preventing weight gain. A diet rich in protein, healthy fats, and fiber can help improve testosterone levels naturally. Regular strength training and cardiovascular exercise are also important for boosting testosterone and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Medications for Hormonal Imbalance: In some cases, medications that help regulate other hormones, like insulin or cortisol, may be prescribed to support testosterone therapy and improve weight management.
Working closely with a healthcare provider is essential for creating a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of the individual.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes to Manage Weight with Low Testosterone
Alongside medical treatments, diet and lifestyle changes play an essential role in managing weight and improving testosterone levels. Here are some practical tips:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole foods that are rich in nutrients and avoid processed foods. Include healthy fats (such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts), lean proteins (chicken, fish, tofu), and complex carbohydrates (whole grains, vegetables).
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in strength training exercises, such as weightlifting, to build and maintain muscle mass. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is also effective in boosting testosterone levels and burning fat.
- Get Enough Sleep: Testosterone production is closely linked to sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to help optimize hormone production and support metabolic health.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lower testosterone levels and promote fat storage. Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Implementing these lifestyle changes can naturally support testosterone production and help prevent weight gain associated with hormonal imbalance.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Low Testosterone and Weight Gain
If you are experiencing unexplained weight gain, fatigue, mood swings, or other symptoms associated with low testosterone, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Testing for low testosterone can provide a clear diagnosis, and your doctor can recommend treatment options tailored to your needs.
- Get Tested: A blood test can determine whether your testosterone levels are below normal. Your doctor will assess your symptoms and discuss treatment options based on the results.
- Monitor Changes: If you’re undergoing testosterone replacement therapy, it’s important to follow up with your healthcare provider regularly to monitor your progress and ensure your treatment is effective.
Early intervention can prevent long-term complications and improve your overall quality of life.
Conclusion:
Low testosterone levels are closely linked to weight gain, particularly in the form of increased abdominal fat and a reduction in muscle mass. Understanding the relationship between testosterone and weight is key to managing your health. If you’re struggling with weight gain and suspect low testosterone, treatment options such as testosterone replacement therapy, lifestyle changes, and proper medical guidance can help restore balance and improve your health. By addressing hormonal imbalances, you can regain control over your weight and overall well-being.


























